Factors That Relate to Body Mass Index
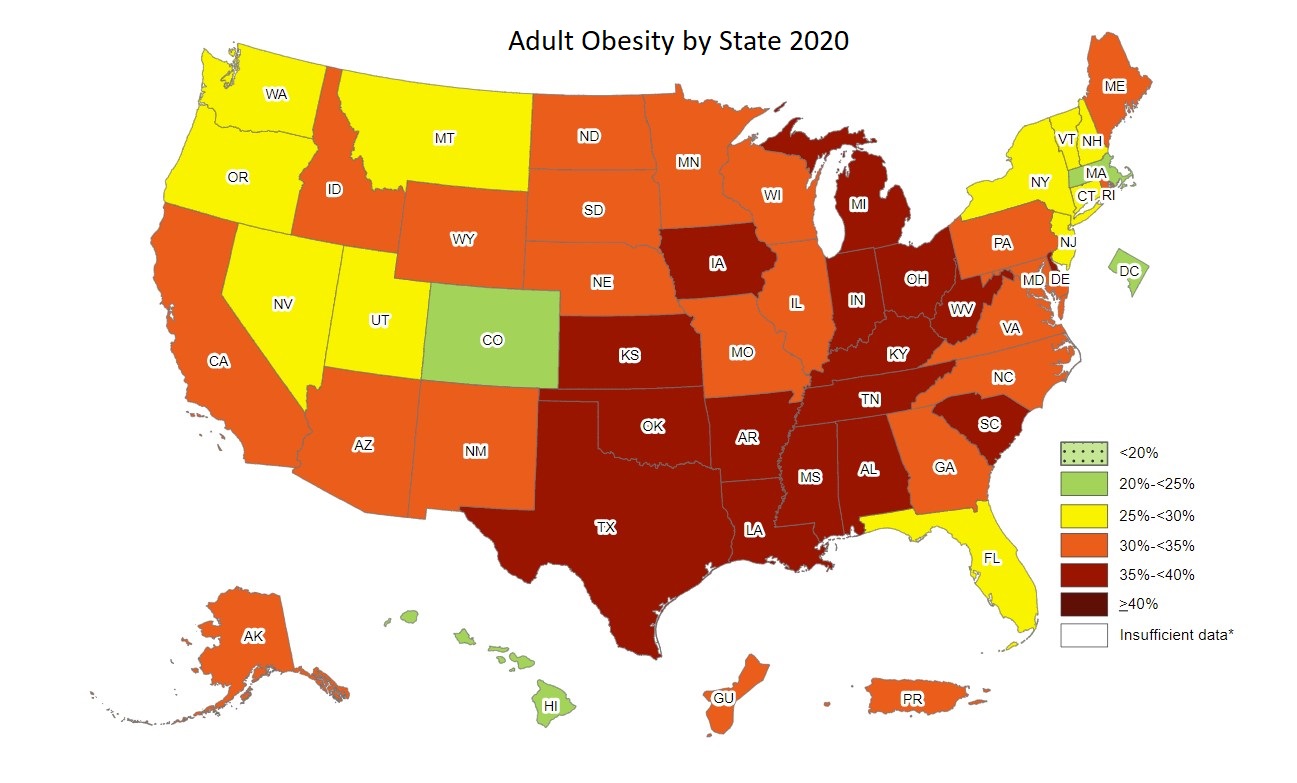
[13]
Introduction
Data Sources and Methods
Feature Selections and Data Cleansing
Data Analysis and Visualization
Discussion 1
Discussion 2
Discussion 3
Discussion 4
Introduction
The problem of obesity has increased significantly in this century. In the United States, obesity grew from 30.5% to 42.4% and severe obesity jumped from 4.7% to 9.2% from 1999 to 2018,[1] as indicated by increased body mass index(BMI) in the population.
That poses a serious health risk in light of the fact that
obesity is correlated with various diseases, such as high blood pressure, diabetes, heart attacks etc. To address the health risk, we have to look at the causes of high BMI and what we can do to prevent obesity. To that end, we searched the internet for information and found the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES).[2]
NHANES is an annual survey taken by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention(CDC). The survey is a program that is designed to assess the health and nutritional status of adults and children in the United States. The program takes a nationwide sample of about five thousand persons each year. Data collected includes demographics, dietary and health related questions and laboratory tests results. Analysis from the survey can be used to determine the risk factors for diseases.
Data Sources and Methods
For this project, we used NHANES 2017 - March 2020 Pre-Pandemic Data[3] There are 82 data sets in the survey. Most of the data sets have about 15 thousand observations and dozens of features. We chose blood pressure, blood glucose, insulin and cholesterol data sets as known factors to examine our methods. We chose diet behavior data sets from NHANES 2011, 2013, 2015 and NHANES 2017 - March 2020 Pre-Pandemic Data as unknown factors to analyze.
There are two main methods in the project.
Body Mass Index(BMI)
$BMI = 703*\frac{weight(lb)}{[height(in)]^{2}}$ [4]
As you can see, BMI is based on two simple factors - height and weight. It's a crude method to roughly estimate body fat. It's not suitable for athletes who might have high BMI with normal body fat or very little body fat. However, "BMI is commonly used by doctors to screen for health problems stemming from weight issues".[5] In this project, we still used BMI to indicate body fat and classify overweight and obesity.
Correlation Coefficient
Correlation coefficients are used to measure the strength of a relationship between two variables.[6] The value of correlation coefficient, r range between -1 and +1. The table below shows that the relationship between two variables based on the value of r:
| Absolute value of r | Strength of relationship |
|---|---|
| r < 0.25 | No relationship |
| 0.25 < r < 0.5 | Weak relationship |
| 0.5 < r < 0.75 | Moderate relationship |
| r > 0.75 | Strong relationship |
[7]
Feature Selections and Data Cleansing
Our original data sets had missing information. We chose features with minimal missing data. As more features were added, the data set became smaller and smaller. The indicators of relationships between BMI and laboratory features changed alightly, but the indicator of BMI and age changed dramatically. We tried different approaches and addressed the problem.
Data Analysis and Visualization
Body Measures
There is a children's BMI category feature in the data, but no adult BMI category. The method we used to classify adult BMI is from National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.[8]
Demographics
We chose seven features, including age, gender, race, marital, and education.
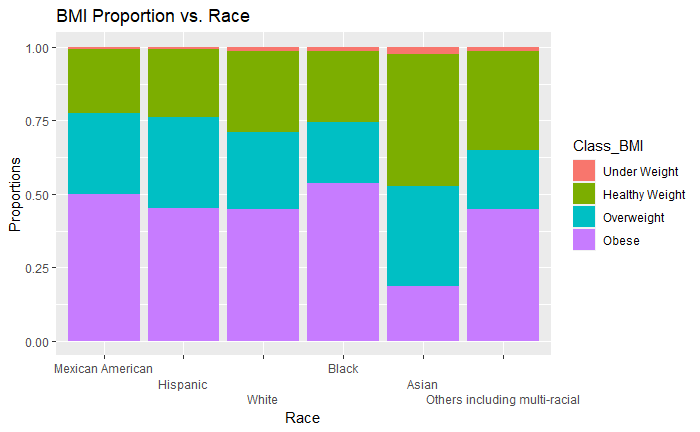
Discussion 1
Asian group is very prominent in the graph.
The percentage of obesity is lower than 25% in the Asian group while around 50% in other races. Also, the percentage of healthy weight in Asian group is about two times of other race groups.
Are Asians healthier than other race groups? Some Asian Americans are in normal weight range, but have less muscle and more body fat.[9] That's another factor that impact the accuracy of BMI.
Insulin and Blood Glucose
We created a new feature, diabetes that is based on blood glucose.[10]
We also apply the same method on it.
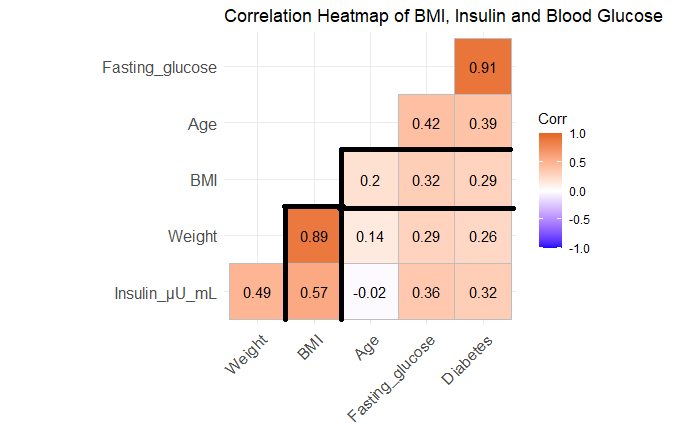
Discussion 2
The graph shows that there's a moderate relationship between BMI and Insulin. But blood glucose and diabetes have a weak relationship with BMI. However, the indicator of relationship between BMI and age is 0.2 which means there's no relationship!
We didn't know what's wrong. In this data set we only dropped some missing values, which is the requirement of performing the method. We wanted to find another material to do the analysis, but it's really difficult to find a data set that contains such comprehensive information and detailed explanation of features. We continued the analysis and hoped the problem can be avoided or addressed.
Total Cholesterol, High Density Cholesterol and Blood Pressure
We added a new feature, cholesterol ratio.[11] In the Blood Pressure data set, both systolic and diastolic were taken three times. We took the average values of each.

Discussion 3
From the graph you can tell that BMI has a weak relationship with cholesterol ratio and blood pressure. But even more bizarre, the indicator of relationship between BMI and age soared from 0.2 to 0.34. Since these are laboratory and examination data, we didn't over-process the data. The big change was dropping missing values. Is this the problem? We decided to add more observations and see what the result will be.
Diet Behaviors
As we mention before, we chose NHANES 2011, 2013, 2015 and NHANES 2017 - March 2020 Pre-Pandemic Data to analyze diet behaviors.
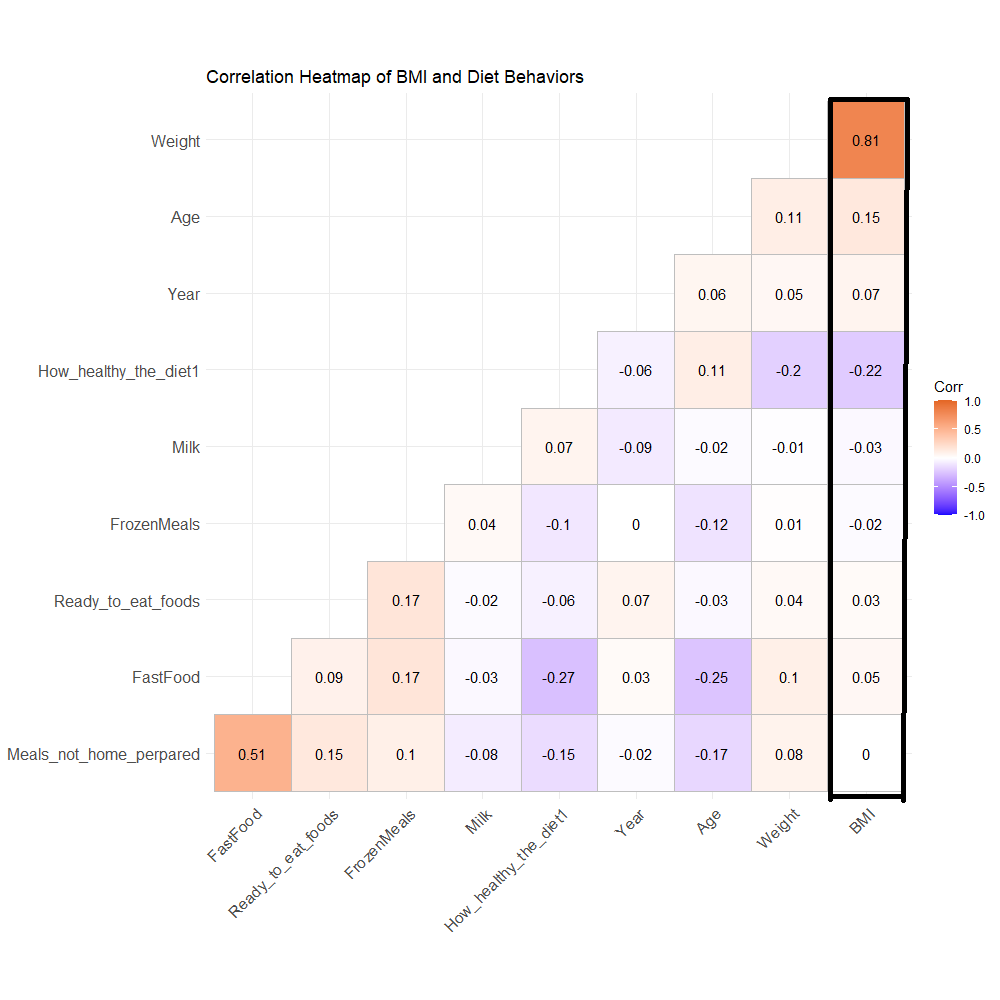
Discussion 4
In this sample, we examine ten diet behaviors, which included the following:
-
- How healthy is your diet?
-
- How much milk did you consumed in the past 30 days?
-
- How many not-home-prepared meals did you consume in the past seven days?
-
- How many of your meals in the past seven days were from fast food or pizza place?
-
- How many of your meals in the past 30 days were from grocery stores(Ready_to_eat_foods)?
-
- How many frozen meals/pizzas did you consume in past 30 days?
From the heatmap you can tell that most of the indicators of these factors are close to zero. The lowest number is from "How healthy is your diet", negative 0.22, which still considered no relationship. We couldn't find any relationship between BMI and the diet behaviors above.
As we all know that what we eat and drink directly impact our weight. Before analyzed the dataset, we expected to build a predictive model based on some diet behaviors. However, we couldn't find any proof that the diet behaviors from NHANES impact BMI. We are of the opinion that those questions didn't relate to body weight. If we want to measure the relationship between BMI and diet behaviors, we need to ask specific questions, such as the proportion of protein or carbohydrate in your diet, how much calories do you consume daily, when do you have breakfast or dinner, etc.
In this graph, the correlation coefficient between age and BMI is 0.15. Since it’s from a bigger dataset, which combined four datasets, we believe that 0.15 is more accurate. Previous correlation heat maps were from different subsets, that joined insulin or blood pressure, which makes the subsets bias.
Summary
table, th, td {
border: 1px solid white;
border-collapse: collapse;
}
th, td {
background-color: #F7F0E5;
}
| Factors | Correlation Coefficient with BMI | Strength of relationship |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | 0.81 or 0.9 | Strong relationship |
| Age | o.15, 0.2 or o.34 | No relationship or Weak relationship |
| Blood glucose | 0.32 | Weak relationship |
| Insulin | 0.57 | Moderate relationship |
| Diabetes | 0.29 | Weak relationship |
| Cholesterol ratio | 0.4 | Weak relationship |
| Systolic | 0.27 | Weak relationship |
| Diastolic | 0.4 | Weak relationship |
| How healthy is your diet? | -0.22 | No relationship |
| How much milk did you consumed in the past 30 days? | -0.03 | No relationship |
| How many not-home-prepared meals did you consume in the past seven days? | 0 | No relationship |
| How many of your meals in the past seven days were from fast food or pizza place? | 0.05 | No relationship |
| How many of your meals in the past 30 days were from grocery stores(Ready_to_eat_foods)? | 0.03 | No relationship |
| How many frozen meals/pizzas did you consume in past 30 days? | -0.02 | No relationship |
References
[1]Obesity is a common, serious, and costly disease
[2]NHANES - About the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
[4]Calculating BMI using the English System
[5]How BMI Impacts Sports and How Much You Should Depend on It
[6]Correlation Coefficient: Simple Definition, Formula, Easy Steps
[7]What is Considered to Be a “Strong” Correlation?
[8]Calculate Your Body Mass Index
[9]Diabetes and Asian Americans
[10]Tests for Type 1 Diabetes, Type 2 Diabetes, and Prediabetes
[11]Understanding the Cholesterol Ratio: What It Is and Why It’s Important

